Floating rate debt is considered to have determinable payments and can therefore be included in the held-to-maturity category. These include financial assets that the entity either holds for trading purposes or upon initial recognition it designates as at fair value through profit or loss. Consider an entity that prepares for future capital expenditure and plans to invest its excess cash in both short and long-term financial assets. This strategy is tailored to fund the anticipated expenditure by balancing the collection of contractual cash flows with the opportunistic selling of financial assets.
Agencies approve final rule to simplify and tailor the “Volcker Rule”
An operating cycle, also referred to as the cash conversion cycle, is the time it takes a company to purchase inventory and convert it to cash from sales. An example of a current liability is money owed to suppliers in the form of accounts payable. A change in business model can be exemplified by scenarios such as an entity shifting from holding commercial loans for short-term sale to acquiring them for long-term cash flow collection. This is seen when an entity acquires a company that manages loans differently, leading to a strategic change in managing their loan portfolio.
Recognition
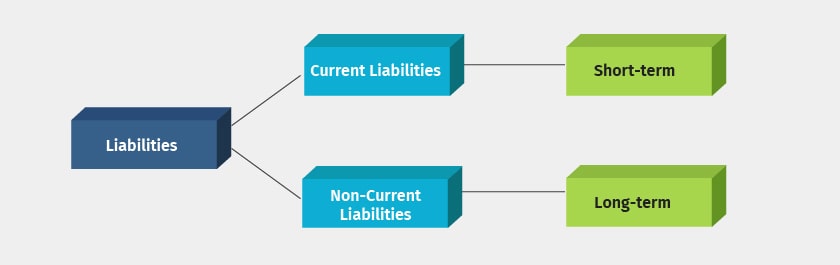
They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses. The above discussions set out the basic principles for the application of IAS 39, the recognition of a financial asset or financial liability in the balance sheet and the classification and measurement of a financial asset or financial liability into different categories. These principles are an important underpinning for the further development of knowledge in this area. Although the current and quick ratios show how well a company converts its current assets to pay current liabilities, it’s critical to compare the ratios to companies within the same industry. The quick ratio is the same formula as the current ratio, except that it subtracts the value of total inventories beforehand. The quick ratio is a more conservative measure for liquidity since it only includes the current assets that can quickly be converted to cash to pay off current liabilities.
- Notably, there is no predefined threshold for sales frequency or volume in this model, as both collecting cash flows and selling assets are fundamental to achieving its intended goals (IFRS 9.B4.1.4A-C).
- IFRS 7.12B-D detail the disclosure requirements relating to the reclassification of financial assets.
- Below is a current liabilities example using the consolidated balance sheet of Macy’s Inc. (M) from the company’s 10-Q report reported on Aug. 3, 2019.
- Furthermore, sales made close to maturity that approximate the collection of the remaining contractual cash flows also align with this business model’s objective.
- It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables.
- Certain services may not be available to attest clients under the rules and regulations of public accounting.
Categories of financial liabilities under IFRS 9
This is the discount rate that will give a present value of the future cash flows that equals the purchase price. Suppose a company receives tax preparation services from its external auditor, to whom it how to apply for a colorado sales tax license must pay $1 million within the next 60 days. The company’s accountants record a $1 million debit entry to the audit expense account and a $1 million credit entry to the other current liabilities account.
Liabilities are a vital aspect of a company because they’re used to finance operations and pay for large expansions. A wine supplier typically doesn’t demand payment when it sells a case of wine to a restaurant and delivers the goods. It invoices the restaurant for the purchase to streamline the drop-off and make paying easier for the restaurant. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
Underwriting and Market-Making Exemptions
Non-current liabilities are due in more than one year and most often include debt repayments and deferred payments. A liability is generally an obligation between one party and another that’s not yet completed or paid. A financial liability is also an obligation in the world of accounting but it’s defined more by previous business transactions, events, sales, exchange of assets or services, or anything that would provide economic benefit at a later date. A liability is something that a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services.

The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations. It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables. The assessment of an entity’s business model for managing financial assets is a fact-based exercise, not merely an assertion. This assessment is evident through the activities conducted to meet the business model’s objectives and requires judgment. An entity must consider all relevant evidence available at the time of assessment.
This is because managing credit risk is integral to ensuring the collection of contractual cash flows. Notably, the final rule entirely eliminates the “enhanced” compliance program requirements, which are currently applicable to banking entities with over $50 billion in total consolidated assets or significant trading assets and liabilities. When an entity’s actions cast doubt on its intent or ability to hold investments to maturity, the entity is prohibited from using the held-to-maturity category for a reasonable period of time. A penalty is therefore effectively imposed for a change in management’s intention.
Trading assets are found on the balance sheet and are considered current assets because they are meant to be bought and sold quickly for a profit. While in the firm’s possession, trading assets should be valued at market value and the value should be updated on the balance sheet every reporting period. If the value of trading assets decreases or increases in the market, not only is the value of the assets adjusted on the balance sheet but this loss or gain, even if only on paper, needs to be recorded on the income statement. For example, banks want to know before extending credit whether a company is collecting—or getting paid—for its accounts receivable in a timely manner. On the other hand, on-time payment of the company’s payables is important as well.